Announcing a massive update to our already comprehensive on-set audio recording series. Engaging video tutorials feature Academy Award and Emmy winning filmmakers who methodically reveal industry best practices and techniques for recording high quality audio on set.

Lesson 1
The Physics of Sound
Before students can learn how to record sound, they need to understand how sound works. This lesson covers the the sound wave, how it can be measured and ultimately, how it is manipulated and captured to create emotion through story. (26:01)
This lesson covers:
- What is sound
- The sound wave
- Frequency and amplitude
- The human hear and its limitations
- Measuring loudness
Lesson 2
How Microphones Work
Microphones are incredible devices that convert sound energy into electrical energy and can do so in different ways. In this lesson, we explore how microphones capture sound, how that sound is converted into energy, and the strengths and weaknesses of each microphone type. (23:52)
This lesson covers:
- How microphones work
- How a dynamic microphone works
- How a condenser microphone works
- How a ribbon microphone works
- What is the signal-to-noise ratio
- What is sensitivity and how is it measured
- What is the maximum sound pressure level
- What is frequency response

Lesson 3
Microphone Pick-Up Patterns
- How pick-up patterns work
- Omnidirectional mics
- Cardioid mics
- Hypercardioid mics
- Shotgun mics
- Figure of 8 mics
- Multi-pattern mics
- How to choose the best pick-up pattern for your shoot

Lesson 4
Audio Pre-Production
- How to break down the script
- What to look for in each scene and how to determine the sound recording requirements
- How to conduct a location scout
- What problematic sounds to look for
- How to deal with ambient sounds and reverb on location
- How to work with a rental facility
- How to track audio equipment
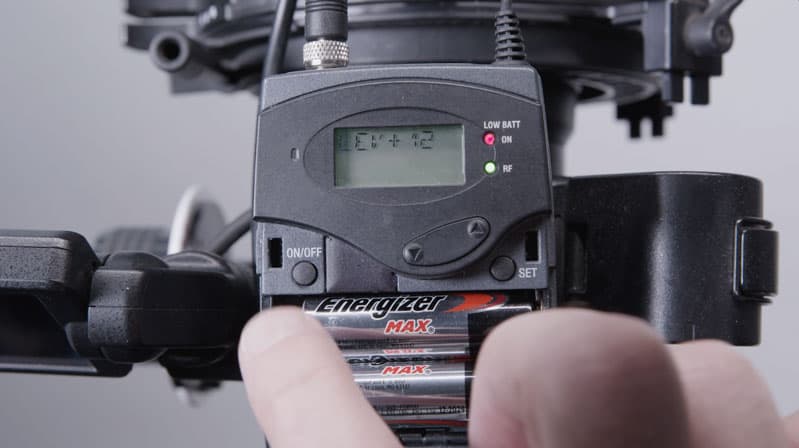

Lesson 5
Lavalier Microphones
- How lavalier microphones work
- Whether to choose a transparent or a proximity lav
- The difference between wired and wireless lavaliers
- How to rig both exposed and hidden lavaliers both on set and on actors
- How to avoid common problems with fabric rubbing against the mic and which fabrics can cause interference
- Issues with wireless systems and how to avoid problems
- Issues with multipath interference and how to avoid it

Lesson 6
The Microphone Boom
- The types of boom poles available
- The types of shock mounts and how they work
- How to mount a microphone in a shock mount
- The ideal microphone pick-up pattern to use on a boom pole
- The types of wind reduction tools and how to use them including
- Wind screens
- Fuzzies
- Zeppelins and dead cats
- Techniques for monitoring audio

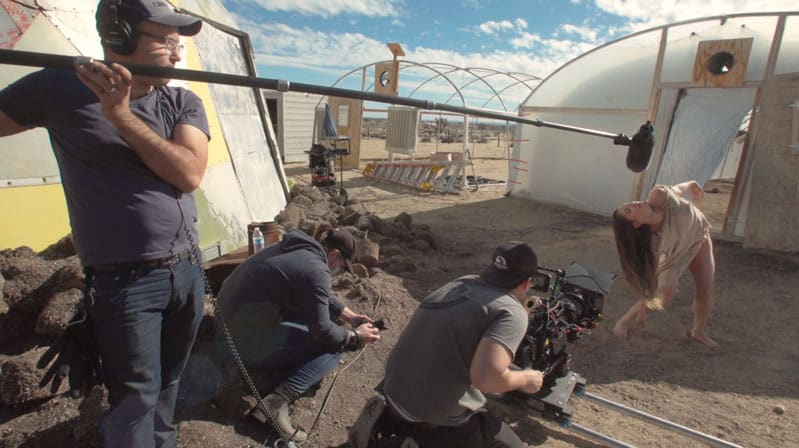
Lesson 7
Boom Operating Techniques
At first glance, the boom mic seems to be fairly simple and straightforward to operate. In actuality, however, it is a tricky skill that balances the ideal mic placement with the movements of the operator. In this lesson, we examine the proper technique for using a boom pole to record on-set audio.
- The various positions for a boom mic
- How to properly place the microphone
- Boom operating etiquette
- How to deal with shadows and reflections
- Communications techniques with the camera operator
- What not to do on set

Lesson 8
Location Recording Techniques
Recording location sound is a challenging process – you need to contend with wind, traffic noise, and compete against the general ambience of the location to record clean dialogue. The decisions you make on set can either make the post-production process easy or add tens of thousands of dollars to your budget trying to fix problems that could have been avoided. In this lesson, learn how to properly prepare for a shoot – the type of gear you’ll need, how to conduct a location scout, and tips for minimizing location noise. (28:17)
- How to control microphone perspective
- How to conduct a sound check and set the levels
- Techniques for monitoring audio
- How to record multiple actors
- What to do if there’s “no sound” in the scene
- The importance of room tone and how to record it
- How to fight the “fix-it-in-post” mentality

Lesson 9
Recording the Audio
Once the microphone picks-up sound, it is then encoded into either an analog or digital signal, then recorded to a device. With advancements in technology, the quality of the recorded signal can be virtually indistinguishable from the original sound. In this module, we explore how sound is recorded and encoded. (37:58)
- The difference between an analog and digital signal
- How to set proper audio levels
- What is the noise floor and how it can adversely affect your audio
- What is the sample rate and bit depth of a digital signal
- What is auto gain
- How compressors and limiters work
- What happens when audio peaks
- What is the dynamic range of the recorded sound and recording medium
- How to determine the gain structure in your audio device chain
- How bars and tone work
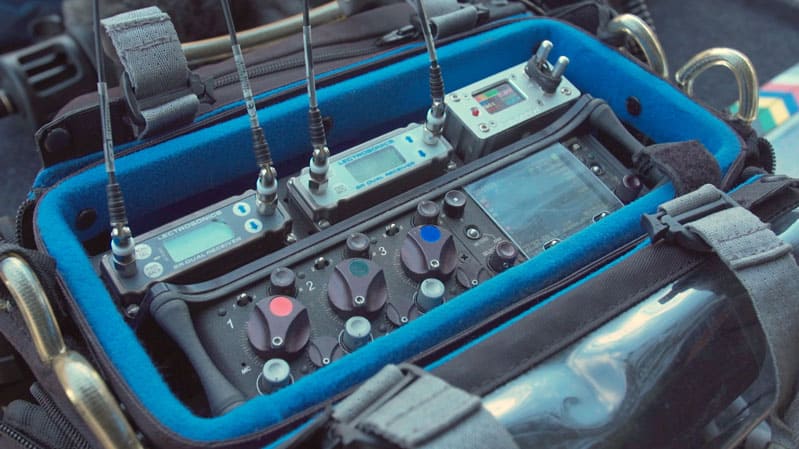

Lesson 10
Audio Configurations
Audio can be recorded many ways – directly into the camera, through a mixer, and/or to a separate recording device. In this module, you will learn common techniques for recording sound, how to manage line/mic level inputs, work with dumb and smart slates, and work with timecode. (20:00)
- The differences between single and dual system recording
- Recording configuration techniques
- How to work with Line/Mic level inputs
- Working with dumb and smart slates
- Working with Timecode
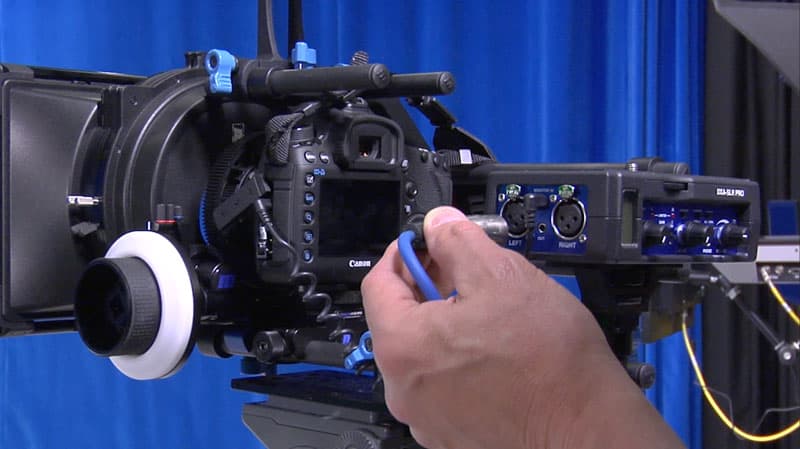

Lesson 11
Cables and Adapters
It’s so easy to focus on the specifications and quality of both the microphone and the recording device that you forget about the cables that connect them. Cables, although seemingly the least interesting equipment can make or break your shoot. In this module, we’re going to look at the types of cables, and connectors, when to use them, and how to care for them. (21:16)
- The various cable types
- The difference between male and female connections
- Adapters and which ones to use
- How to adapt cables for DSLR cameras
- Cable care
- How to work with breakaways


